
In the era of Industry 4.0, where intelligent automation, data analytics, and connectivity define modern manufacturing, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) have emerged as the central foundation driving this transformation. By integrating physical processes with computational intelligence, CPS is revolutionizing the way industries design, produce, and maintain systems.
This blog explores what CPS is, how it works, and its growing significance in shaping the future of industrial automation and smart manufacturing.
Cyber-Physical Systems are integrated frameworks that connect the physical world (machines, sensors, actuators) with the cyber world (software, algorithms, data analytics).
They form a continuous feedback loop where physical actions generate data that is analyzed digitally, leading to real-time decision-making and optimization. In simple terms, CPS allows machines to **sense, process, and act intelligently** — making factories and industrial environments self-aware and adaptive.
Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution, marked by the fusion of digital and physical systems. CPS serves as its technological backbone by enabling smart manufacturing ecosystems that operate autonomously, efficiently, and sustainably.
A typical CPS architecture consists of three main layers:
| Layer | Function | Key Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Layer | Data collection through embedded sensors and devices | Sensors, actuators, PLCs |
| Cyber Layer | Data analysis, computation, and modeling | Cloud computing, AI/ML, Edge processing |
| Communication Layer | Data transfer and synchronization | IoT, 5G, Industrial Ethernet, MQTT |
| Control & Decision Layer | Implements optimized decisions | Predictive algorithms, control systems |
| Human Interaction Layer | Supervision and feedback | Dashboards, AR/VR systems, HMIs |
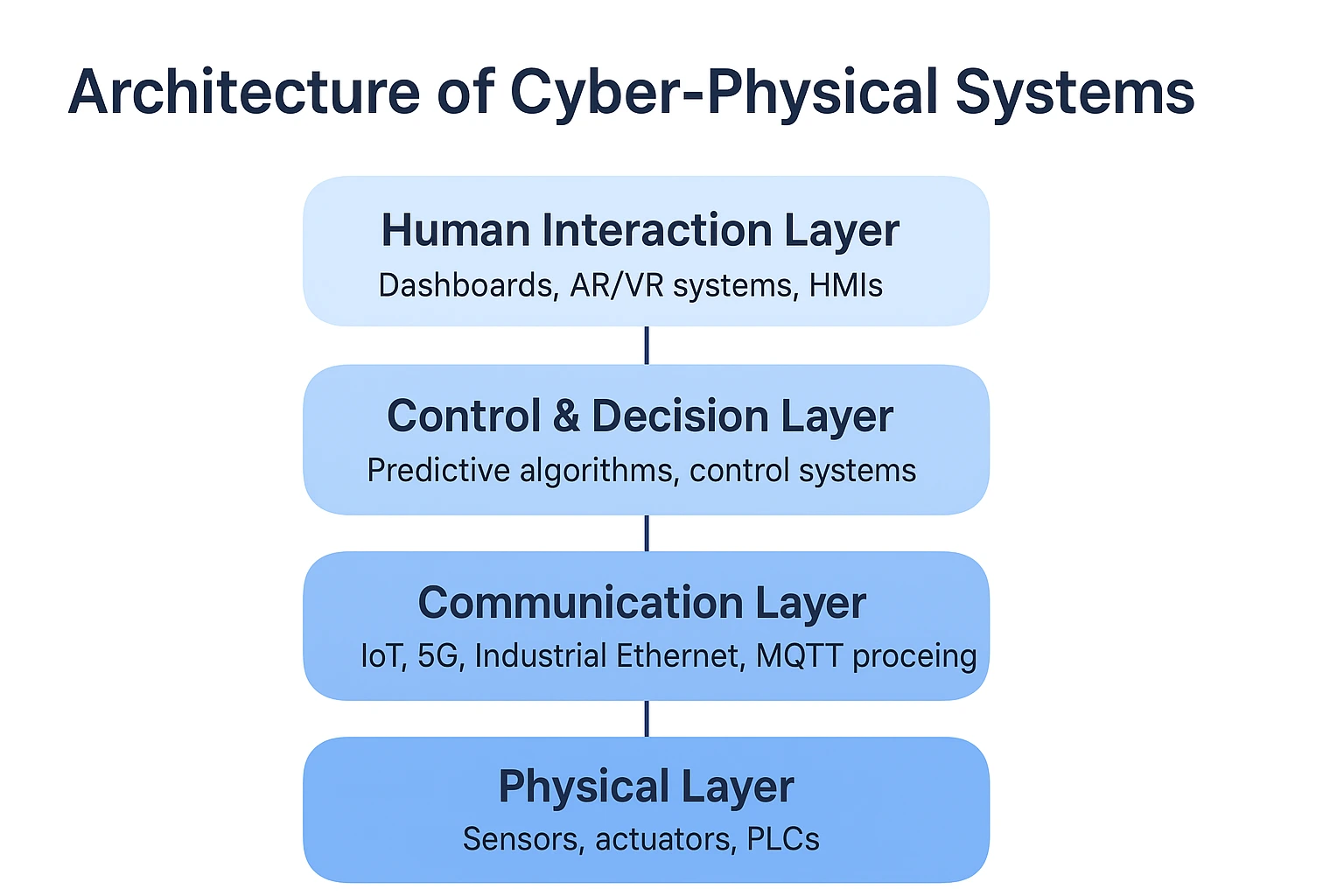
This multi-layered architecture ensures coordination between the physical and virtual environments, making systems resilient, intelligent, and adaptive.
CPS has wide-ranging applications across industrial domains, reshaping processes from design to delivery.
a. Smart Manufacturing
Machines equipped with sensors and controllers can communicate autonomously to streamline production.
Example: A robotic arm detecting a fault in the assembly line can alert other systems and trigger automatic recalibration.
b. Predictive Maintenance
By analyzing sensor data, CPS predicts machine wear and tear before breakdowns occur, reducing downtime and saving costs.
Example: Siemens and General Electric use CPS-enabled systems for proactive turbine and motor maintenance.
c. Intelligent Transportation Systems
CPS enhances logistics and traffic management through real-time vehicle tracking, route optimization, and automated fleet control.
Example: Smart traffic lights connected to CPS networks can reduce congestion and accidents.
d. Healthcare Systems
In medical CPS, wearable devices monitor vital signs and transmit data for instant diagnosis and emergency response.
Example: Remote surgery assisted by robotic systems connected through CPS ensures accuracy and speed.
e. Energy Management
CPS enables smart grids that dynamically balance supply and demand.
Example: Smart meters automatically adjust power distribution, optimizing energy use and reducing waste.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Control | Immediate response to operational changes or anomalies |
| Efficiency Enhancement | Automation reduces human error and production time |
| Cost Optimization | Predictive analytics minimizes maintenance and resource wastage |
| Increased Flexibility | Rapid adaptation to new product lines or configurations |
| Improved Quality | Consistent monitoring ensures precision and compliance |
| Sustainability | Reduced energy consumption and carbon footprint through smart optimization |
Despite its enormous potential, deploying CPS comes with significant challenges:
The future of CPS lies in greater autonomy, intelligence, and human collaboration. With the advent of 5G networks, edge computing, and AI integration, CPS will enable industries to function as **self-learning ecosystems** capable of decision-making without human intervention.
Emerging trends include:
In essence, CPS will continue to evolve as the core driver of smart factories, sustainable infrastructure, and intelligent manufacturing — pushing Industry 4.0 toward its full potential.
Cyber-Physical Systems are not just a technological advancement but a paradigm shift in industrial evolution. By merging computation, communication, and control, CPS enables industries to become smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable. As we move toward Industry 5.0, CPS will serve as the foundation for human-machine collaboration and truly intelligent production systems.
1. What are Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)?
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are intelligent systems that integrate physical components (like machines or sensors) with digital control and communication networks. They allow real-time data monitoring, decision-making, and automation in industries.
2. How do CPS contribute to Industry 4.0?
CPS form the foundation of Industry 4.0 by connecting machines, humans, and networks. They enable automation, predictive maintenance, and smart manufacturing, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
3. What are some real-world examples of CPS?
Examples include self-driving vehicles, smart grids, automated manufacturing systems, and medical monitoring devices that collect and analyze data in real-time.
4. What technologies support Cyber-Physical Systems?
Key technologies include the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning, Edge Computing, and Cloud Infrastructure, all of which enhance system performance and communication.
5. What are the major benefits of CPS in industries?
CPS provide higher productivity, energy efficiency, predictive maintenance, improved safety, and seamless data integration across production processes.
6. Are there any challenges in implementing CPS?
Yes. The main challenges are cybersecurity threats, high implementation costs, data privacy issues, and the need for a highly skilled workforce.
7. What industries benefit the most from CPS?
Manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, energy, and agriculture are some of the sectors where CPS play a crucial role in automation and intelligent decision-making.
8. What is the future of CPS in Industry 4.0?
The future of CPS lies in deeper integration with AI and digital twins, allowing industries to achieve fully autonomous and adaptive production systems.
Explore more resources on Industry 4.0 and advanced engineering technologies:

|
Citation Indices
|
All
|
Since 2020
|
Citation |
2359 |
1680 |
h-index |
19 |
15 |
i10-index |
57 |
24 |
|
Acceptance Rate (By Year)
|
|
|
Year
|
Percentage
|
|
2023
|
9.64%
|
|
2027
|
17.64%
|
|
2022
|
13.14%
|
|
2021
|
14.26%
|
|
2020
|
11.8%
|
|
2019
|
16.3%
|
|
2018
|
18.65%
|
|
2017
|
15.9%
|
|
2016
|
20.9%
|
|
2015
|
22.5%
|